what is ASTAXANTHIN?
Worldwide it is being called a superantioxidant, the king of antioxidants, the no.1 antioxidant you haven’t heard about but need to use, a miracle drug for everything from wrinkles to dementia and age-related vision loss. Studies show that it really can fight several diseases.

what is ASTAXANTHIN?

Worldwide it is being called a superantioxidant, the king of antioxidants, the no.1 antioxidant you haven’t heard about but need to use, a miracle drug for everything from wrinkles to dementia and age-related vision loss. Studies show that it really can fight several diseases.
WHAT IS ASTAXANTHIN?
HOW DOES THE PUREST AND MOST POWERFUL ANTIOXIDANT FOUND IN NATURE ACTUALLY WORK?
HOW IS ASTAXANTHIN OBTAINED?
HOW TO CHOOSE ASTAXANTHIN PRODUCTS?
ASTAXANTHIN'S FAME
DISCOVERY OF ASTAXANTHIN
Benefits provided by ASTAXANTHIN
Astaxanthin is one of the most powerful antioxidants found in nature. The highest concentration of this substance is found in single-cell microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis, which has been recognised as the environmentally best source of extracting the purest and most effective astaxanthin. These algae produce large amounts of astaxanthin for self-preservation purposes to protect their cell DNA in the battle with huge oxidative stress from UV radiation and free radicals. Astaxanthin is also found in marine inhabitants (wild salmon, trout, krill, shrimp, lobster and crab) that have free access to feed on these microalgae. This is the pigment responsible for the reddish colour of the abovementioned crustaceans and fish.
Astaxanthin is a carotenoid and is closely related to all known beta-carotenes and lutein. As a carotenoid astaxanthin is a powerful antioxidant. It protects cells from damage caused by unstable molecules called free radicals. However, unlike other carotenoids, which under certain conditions can themselves trigger free radical activity, astaxanthin is a completely pure antioxidant – it only protects and never acts as a pro-oxidant.
Astaxanthin provides powerful natural protection against the harm caused by free radicals – so-called oxidative stress. It is the most powerful free radical scavenger of all anti-aging molecules; it is 65 times stronger than vitamin C, 14 times stronger than vitamin E, 54 times stronger than beta-carotene, 20-50 times stronger than synthetic astaxanthin1

1. OXYGEN FREE RADICAL SCAVENGING ABILITIES OF VITAMINS C, E, b-CAROTENE, PYCNOGENOL, GRAPE SEED PROANTHOCYANIDIN EXTRACT AND ASTAXANTHINS IN VITRO. Debasis Bagchi, Ph.D. Pharmacy Sciences, Creighton University School of Health Sciences, June 2001
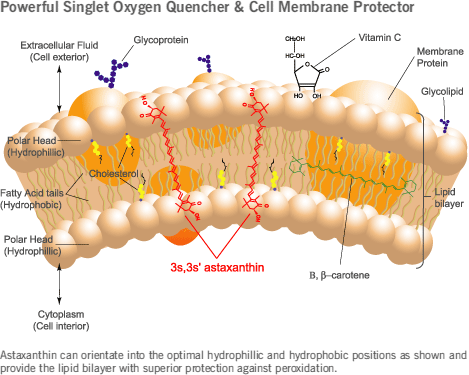
Astaxanthin scavenges for free radicals in the water-loving (hydrophilic) end of the cell membrane, as well as in the fat-loving (lipophilic) end – unlike many other antioxidants, which only work either inside the membrane (vitamin E and beta-carotene) or on the outside (vitamin C). This ability is due to astaxanthin’s unique structure – thanks to the polarity at each end of its long molecule, astaxanthin can lodge itself both on the inner and outer level of the cell membrane. Furthermore, unlike other antioxidants (vitamins C and E and beta-carotene) astaxanthin never becomes a pro-oxidant, i.e. a promotor of free radicals.
Astaxanthin can be obtained in two ways – naturally as a gift of nature or artificially through chemical synthesis.
Naturally obtained astaxanthin from microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis.
The algae are specially cultivated for this purpose. When the algae in the container has grown to about the size of a nut and are a nice red colour, the extract is prepared. The extract in LYL ASTAXAN is obtained by the most effective method – the unique and eco-friendly DeepExtract™ ultra high pressure carbon dioxide extraction technique. This has several implications. First of all, no chemical solvents are used in the extraction process, therefore 100% purity of the product is guaranteed. Secondly, oxygen-free conditions and a moderate temperature at the time of extraction safeguard the bioactivity of the astaxanthin and also ensure a higher concentration of the active substance.
On average each capsule contains 4.4 mg of astaxanthin, as well as other valuable natural substances found in microalgae. Finally, this method guarantees that the composition of the extract remains invariable regardless of the changes in nature conditions at the time of extraction. The end result is a marine carotenoid mixture that contains the bright red astaxanthin extract – its oleoresin – which is made up of 90% astaxanthin and other antioxidants, including lutein and carotenes. This extract does not contain any artificial additives or pigments. The LYL love your life® product line’s astaxanthin LYL ASTAXAN® available in Latvia is obtained by the method described above.
When choosing another manufacturer’s product attention needs to be given to whether the algae has not been grown in open reservoirs where they can be subjected to air pollution and many foreign bodies (dust, insects, etc.) have access to the pool.
Although marine flora and fauna are the best sources of astaxanthin, it can also be obtained from Phaffia yeast. Unfortunately, the content of astaxanthin in the yeast is only approximately 40%, which is just half of the amount found in the microalgae.
Artificial astaxanthin
Astaxanthin can be produced through artificial chemical synthesis. Sadly there is no legislative obligation to indicate which type of astaxanthin – natural or synthetic – a product contains. The only way to try to differentiate between natural and synthetic astaxanthin is the price of the product: artificial astaxanthin is cheaper. There is a significant difference in the effects of natural and synthetic astaxanthin. Natural astaxanthin derived from microalgae is up to 50 times more potent than its synthetic counterpart. The effective and wide-ranging effects of astaxanthin have been documented only in studies using natural astaxanthin.
Astaxanthin came to fame in 2011 when Oprah Winfrey together with dermatologist Nicholas Perricone revealed the miracle to the public on her TV show. Since then interest in astaxanthin has skyrocketed. It has been called a miracle drug by celebrities and world-class athletes.
More and more celebrities are testifying that they owe their good looks to astaxanthin. In interviews, books and blogs supermodel Heidi Klum and actress Gwyneth Paltrow have not hesitated to reveal that astaxanthin is the key to their beauty and have praised its effects. Pop icon Madonna says that astaxanthin provides her with the strength and energy she needs to work out for several hours each day.
The Swedish Olympic ski team has been using astaxanthin since 1995. Triathlete Tim Marr has called astaxanthin his favourite tool in improving his athletic performance. Marathon runner Jonathan Liau affirms that astaxanthin helps achieve better results despite age and removes the need for other dietary supplements such as glucosamine as it also ensures healthy joints.
Whatever image may have been created, astaxanthin is not a new discovery.
It has since long been known in most parts of Asia, including Japan. Astaxanthin – the secret to beauty and youth – has remained hidden from the rest of the world, while being developed and tweaked in this region. Here, having discovered the effects of the king of antioxidants, women have been using it daily for years. In Asia astaxanthin is recommended for anyone who wishes to retain youthful skin (and more) as the most powerful antioxidant in the world – astaxanthin – combats free radicals before they manage to harm the collagen layer in skin. It is widely known that collagen is crucial for maintaining smooth and elastic skin.
Healthy skin and the resulting improved appearance is merely one of the many benefits provided by natural astaxanthin. Scientific studies have been carried out in order to assess the effects of using astaxanthin. The results show that this antioxidant has a much more extensive impact on the human body than initially presumed.
Studies have concluded that astaxanthin has a positive effect on skin health and appearance, vision and eye health, physical endurance and improved metabolism, cardiovascular health, the immune system, brain health, gastrointestinal health, improved memory and mental capacity, it helps treat male infertility and stops development of cancer cells.
- protects cells against oxidative stress;
- delays aging of skin caused by UV radiation – stimulates production of collagen and protects dermal fibroblasts thus improving skin moisture, elasticity and microtexture, reducing “crow’s feet”, loss of moisture, discoloration, risk of skin cancer;
- promotes normal functioning of the nervous system;
- by protecting brain tissue, improves brain and psychosomatic function in seniors, reduces forgetfulness;
- in case of Alzheimer’s – it reduces the level of beta-amyloids in the blood, which block oxygen supply to brain tissue;
- promotes normal psychological functioning;
- promotes normal functioning of the immune system, also during and after intense physical activity;
- in cases of chronic disease such as asthma or allergies reduces the excessive activity of the immune system;
- helps ensure normal metabolic energy production;
- maintains heart health and reduces risk of heart attack by ensuring normal hemocysteine metabolism;
- normalises the level of blood lipids by reducing the level of triglycerides and “bad” LDL cholesterol and improving the level of “good” HDL cholesterol, thus averting formation of concretions in the blood vessels;
- reduces risk of thrombosis by blocking production of enzymes that destabilise concretions;
- improves physical endurance by stimulating use of fat as an energy source and reducing secretion of lactic acid;
- reduces risk of anaemia by stimulating normal production of red blood cells;
- reduces secretion of inflammation inhibitors, including reducing the level of C-reactive protein – a systemic marker of inflammation;
- improves vision, including untreated near- and far-sightedness, reduces symptoms of eye fatigue, improves capillary circulation;
- delays onset of the most common eye diseases – cataract, glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration;
- relieves symptoms of computer vision syndrome;
- for diabetics – reduces the blood glucose level, insulin resistance, general inflammation in the body and oxidative stress, stimulates the ability of the pancreas to produce insulin, reduces risk of diabetic complications, such as nephropathy, cataract, retinopathy and development of heart disease;
- slows development of various types of tumours;
- reduces storage of fat in the liver;
- stimulates the functioning of internal antioxidant systems for people with excess weight;
- protects the mitochondria by delaying oxidation of fatty acids within the mitochondria;
- supresses activation of the inflammatory cascade mediated by NF-kB, which is the main inhibitor of most degenerative diseases;
- promotes functioning of the body’s antioxidant system (synergist) and protects other antioxidants from dissolving too quickly.
